Check Vehicle Insurance Status Online in India
In India, vehicle insurance is legal requirement under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 is not just a financial safeguard. Ensuring your vehicle has valid insurance protects you from damage costs. Check your vehicle insurance status regularly help timely renewals and accident-related claims.
To verify your vehicle insurance status follow these both details online and offline.
Online Methods to Check Vehicle Insurance Status
1. V A H A N | National Register e-Services
A official platform by the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways store vehicle dats. Follow these steps:
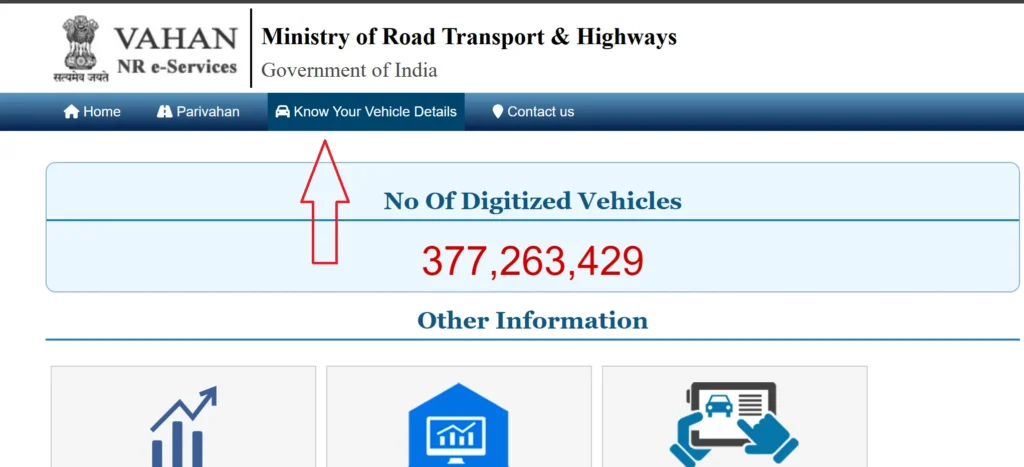
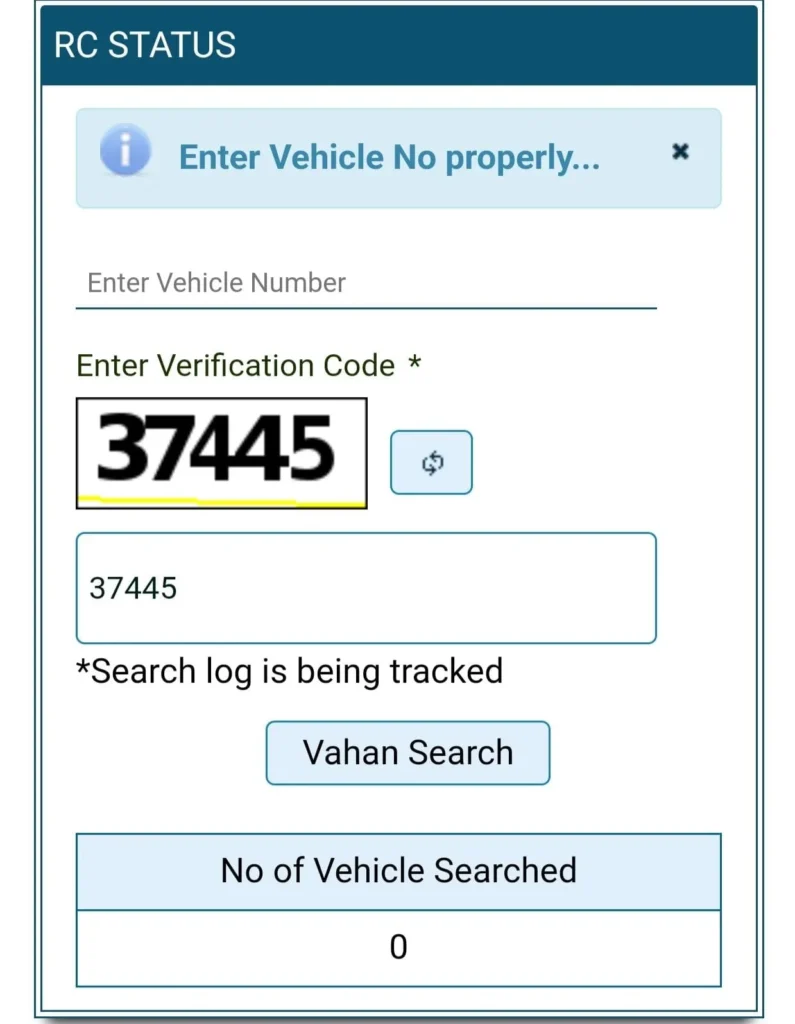
Note
RTO verification is needed in uncomplete data and requires registration number.
2. Insurer’s Website or App
To manage insurance use online portals or mobile apps. Follow these steps:
Popular Insurers:
- Bajaj Allianz: bajajallianz.com
- Reliance General: reliancegeneral.co.in
- Tata AIG: tataaig.com
Offline Methods to Check Vehicle Insurance Status
1. Visit the Regional Transport Office (RTO)
RTOs maintains insurance details or vehicle records. Follow these steps:
Documents Needed:
- Vehicle registration certificate (RC)
- Identity proof
- Insurance policy copy (if available)
2. Contact Insurance Provider
Contact your insurer foe detailed information. Below steps helps you:
3. Visit an Insurance Agent or Broker
If policy buy through agent ask him to check policy status:
Tips for Insurance Status Checks
- Details Required: Policy number, vehicle registration number, chassis/engine number.
- Check Expiry Date: To avoid penalties renew policies on time.
- Verify accuracy: For correct data use (Parivahan portal and insurer portal).
- Careful from Fraud: Use verified contact number and websites.
Difference Between First-Party and Third-Party Vehicle Insurance
Vehicle insurance in India is financial security of your vehicle. Third-party insurance cover damages to other under mandatory under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 or first-party insurance protects the policyholder vehicle.
| Feature | First-Party Insurance | Third-Party Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Policyholder and their vehicle | Third parties (others’ property/people) |
| Scope | Own-damage (accidents, theft, fire, natural disasters) | Damages/injuries caused by your vehicle |
| Legal Requirement | Optional | Mandatory (Motor Vehicles Act, 1988) |
| Exclusions | Third-party damages | Policyholder’s vehicle damage |
| Example | Repairs for your car after a crash | Compensation for hitting another car |
Types of Vehicle Insurance Policies
- Comprehensive Insurance: First-party and third-party coverage Protects your own-damage and third-party.
- Standalone Own-Damage (OD) Insurance: Cover only policyholder vehicle.
- Pay-As-You-Drive Insurance: Premium based on kilometers driven. Best for low-usage vehicles.
- Bundled Policies: Combination of third-party and own-damage for new vehicles (up to 3 years for two-wheelers and 1 year for four-wheelers.
Penalties for Driving Without Valid Insurance
Driving without valid insurance is illegal under the Motor Vehicles Act, 2019. Penalties include:
- First offence: ₹2,000 fine and/or up to 3 months imprisonment.
- Second offense: ₹4,000 fine and/or up to 3 months imprisonment.
Claim Process
- Inform Insurer immediately after incident.
- File FIR for accidents, theft or third-party claims.
- Attach documents policy copy, RC, DL, FIR, repair bills.
- Insurer verify damage for approval.
For more details, visit IRDAI or contact your insurer.